Asexual reproduction is a fascinating & diverse phenomenon found within The animal kingdom. It allows certain species To reproduce without The need for a mate, resulting in The creation of genetically identical offspring. While most commonly observed in simpler organisms such as bacteria & single-celled organisms, asexual reproduction can also occur in more complex animals like insects & lizards. This unique reproductive strategy offers advantages such as rapid population growth & The ability To colonize new habitats. Through exploring The world of asexual reproduction in animals, we gain insight into The incredible adaptability & resourcefulness of these organisms.
Exploring the Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals. Discover The amazing world of asexual reproduction in animals – where organisms can reproduce without a partner. Uncover The fascinating methods & benefits of this unique process, as we delve into The wonders of nature. Join us in this captivating exploration of asexual reproduction, as we unravel The secrets of nature’s incredible abilities.
What is Exploring The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals & how does it work?
Exploring The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals is The study of The reproductive process in which offspring are produced without The involvement of a mate. Unlike sexual reproduction, which requires The fusion of gametes from two individuals, asexual reproduction allows organisms To reproduce on their own, resulting in The production of genetically identical offspring.
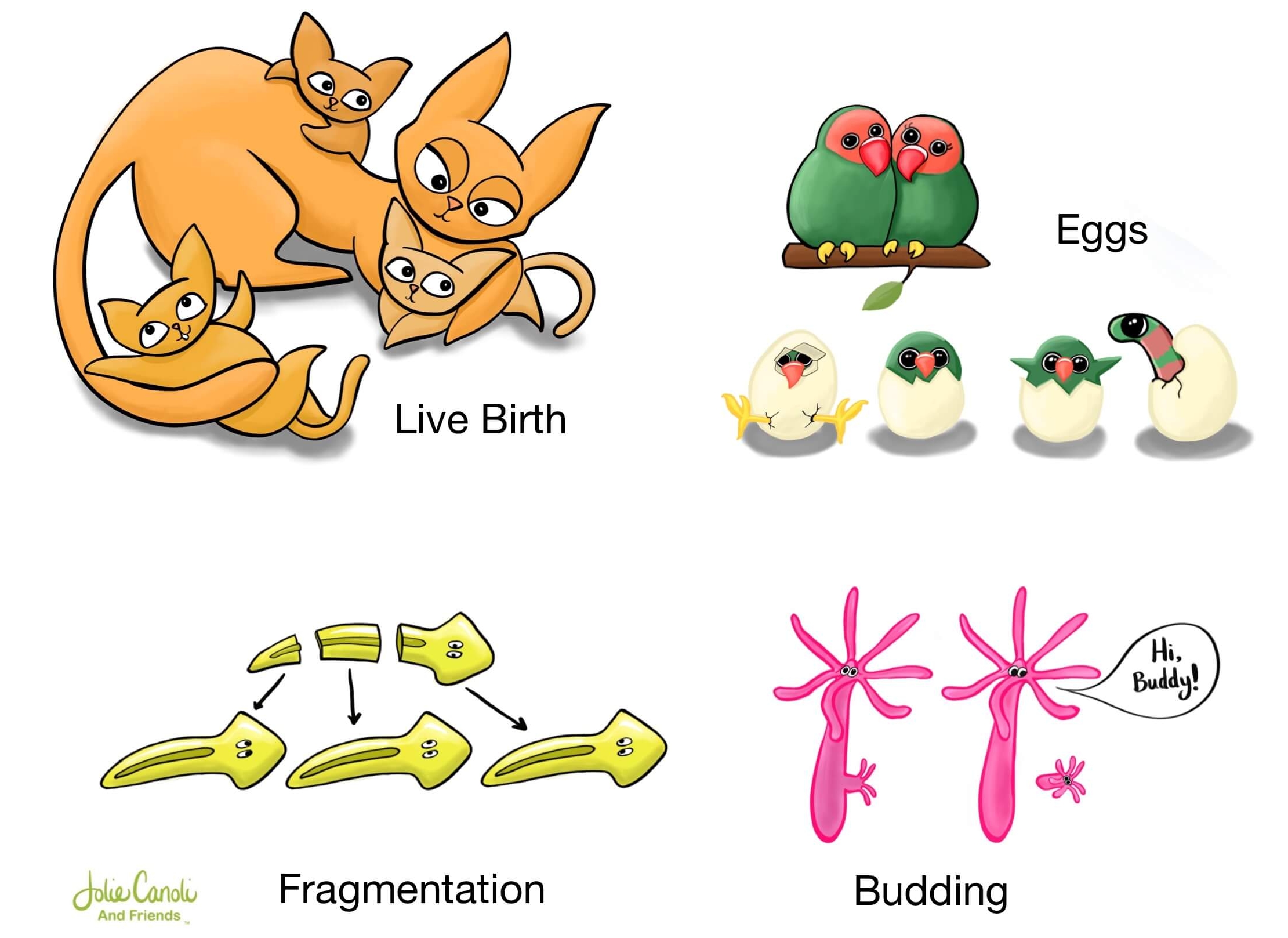
Asexual reproduction in animals can occur through various mechanisms, including binary fission, budding, fragmentation, parthenogenesis, & agamogenesis. Each mechanism involves different processes & adaptations depending on The species.
Binary fission is a common method used by single-celled organisms, such as bacteria & amoebas. It involves The division of a parent cell into two genetically identical daughter cells. This process allows for rapid reproduction & population growth.
Budding occurs when a new individual grows out of The body of The parent organism. The offspring start as a small bud or outgrowth, which eventually detaches & develops into a separate organism. This method is observed in species like hydra & yeast.
Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction that occurs when The body of an organism fragments into multiple pieces, each of which can develop into a new individual. This method is common in many invertebrates such as starfish & planarians.
Parthenogenesis refers To The development of an embryo without fertilization by a male gamete. It is observed in several species of insects, reptiles, & fish. In parthenogenesis, unfertilized eggs develop into viable offspring, with The offspring inheriting genetic material only from The mother.
Agamogenesis is a specialized form of asexual reproduction found in certain insects, such as aphids. It involves The development of embryos without fertilization. The offspring produced are genetically identical To The mother & also female.
A brief history of Exploring The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals
The study of asexual reproduction in animals dates back To ancient times. Empedocles, a Greek philosopher, was one of The first To speculate on The possibility of reproduction without mating. However, it wasn’t until The 19th century that significant progress was made in understanding The mechanisms & implications of asexual reproduction.
In The mid-1800s, German embryologist August Weismann conducted experiments on planarian worms & observed their ability To regenerate & reproduce through fragmentation. This research laid The foundation for further studies on asexual reproduction in animals.
Later, in The early 20th century, scientists such as Jacques Loeb & H.J. Muller made significant contributions To The field of asexual reproduction. Loeb conducted experiments on parthenogenesis in sea urchins, while Muller studied The asexual reproduction of Drosophila fruit flies.
Today, with advancements in molecular biology & genetic research, scientists continue To explore The fascinating world of asexual reproduction in animals, uncovering new insights into The underlying genetic & physiological processes.
How To implement Exploring The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals effectively
Implementing asexual reproduction in animals effectively requires a deep understanding of The specific reproductive mechanisms & adaptations of The chosen species. Here are some key considerations:
1. Selecting suitable species: Different animal species exhibit various forms of asexual reproduction. Choose a species that is well-suited for research or practical applications based on their reproductive characteristics, genetic stability, & adaptability.
2. Creating optimal conditions: Provide The necessary environmental conditions for The chosen species To thrive & reproduce asexually. This may involve maintaining specific temperature, humidity, & nutrient levels.
3. Manipulating reproductive cues: Some animals require specific cues or stimuli To initiate asexual reproduction. Experiment with factors like light, temperature, or chemical signaling To induce The desired reproductive response.
4. Genetic management: Monitor & maintain genetic diversity within a population practicing asexual reproduction. This can be achieved through periodic introduction of genetic material from related populations or manipulating The reproduction process To retain a degree of genetic variation.
5. Monitoring & evaluation: Regularly monitor & evaluate The success & efficiency of The asexual reproduction process. This includes assessing The reproductive rate, genetic stability, & overall health of The population.
The key benefits of using Exploring The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals
Exploring The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals offers several advantages:
1. Rapid population growth: Asexual reproduction allows for exponential population growth, as each individual has The potential To produce numerous identical offspring.
2. Genetic stability: Asexual reproduction ensures genetic stability as there is no genetic recombination or variation introduced through mating. This can be beneficial in maintaining favorable genetic traits within a population.
3. Adaptation To stable environments: Asexual reproduction is particularly advantageous in stable & predictable environments where genetic diversity & The shuffling of genes are not necessary for survival & adaptation.
4. Energy efficiency: Asexual reproduction often requires less energy & resources compared To sexual reproduction, as there is no need To find & attract a mate or produce gametes.
Challenges associated with Exploring The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals & potential solutions
While asexual reproduction offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges associated with its implementation:
1. Limited genetic diversity: Asexual reproduction can lead To limited genetic diversity within a population, which may make The population more susceptible To diseases or environmental changes. To combat this, periodic introduction of genetic material from related populations or using genetic engineering techniques can be employed To maintain diversity.
2. Accumulation of harmful mutations: In The absence of genetic recombination, harmful mutations can accumulate over generations. Regular monitoring of The population & removal of individuals with detrimental mutations can help mitigate this issue.
3. Lack of adaptability To changing environments: Asexual reproduction may hinder The ability of a population To adapt To rapidly changing environments. To address this, hybridization with sexually reproducing individuals or implementation of genetic engineering techniques can introduce new genetic material & increase adaptability.
Future trends & innovations expected in Exploring The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals
The field of asexual reproduction in animals is continually evolving, & several future trends & innovations can be expected:
1. Genetic manipulation: Advancements in genetic engineering techniques will allow for precise manipulation of asexual reproduction processes in animals. This includes introducing specific genetic changes or altering reproductive behaviors To enhance desired traits or adaptability.
2. Artificial reproduction methods: Researchers may develop artificial reproduction methods that mimic natural asexual reproductive processes. This could involve The use of artificial tissues or organs To facilitate The reproduction of specific species.
3. Synthetic biology approaches: Synthetic biology holds great potential in The field of asexual reproduction. Scientists may design & construct artificial organisms capable of asexual reproduction, allowing for controlled & scalable production of desired offspring.
Overall, exploring The fascinating world of asexual reproduction in animals offers valuable insights into The diverse reproductive strategies of different species. By understanding & harnessing these mechanisms, scientists can potentially unlock new possibilities in reproduction & genetics research.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-521096038-b1661ef0f72645739b86ebd4cf81aa5c.jpg)
Exploring The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals
Asexual reproduction is a remarkable biological process used by various animal species To produce offspring without The need for a partner. Unlike sexual reproduction, which involves The fusion of gametes from two individuals, asexual reproduction relies on The ability of an organism To create genetically identical copies of itself.
Types of Asexual Reproduction
There are several types of asexual reproduction that can be observed in The animal kingdom. One common method is binary fission, which is often observed in single-celled organisms like bacteria & protozoa. During binary fission, The parent organism splits into two identical daughter cells.
Another type of asexual reproduction is budding, where new individuals develop from outgrowths known as buds on The parent organism. This process can be seen in organisms such as hydra & yeast. The bud grows, eventually detaches from The parent, & becomes an independent individual.
Fragmentation is yet another form of asexual reproduction, where a parent organism breaks into several fragments, each of which can develop into a new individual. This method is commonly observed in organisms like flatworms & sea stars.
Parthenogenesis is a unique form of asexual reproduction observed in a variety of species, including some insects, reptiles, & fish. In parthenogenesis, unfertilized eggs develop into viable offspring. This process allows females To reproduce without The need for mating with males.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction offers several advantages for animals. One significant advantage is The ability To rapidly produce offspring, allowing for The colonization of new habitats or The exploitation of abundant resources. Since no time or energy is spent on finding a suitable mate, asexual reproduction can be a more efficient & time-saving method.
Additionally, asexual reproduction allows for The preservation of successful traits & adaptations. Offspring produced through asexual reproduction are genetically identical To their parent, ensuring The retention of advantageous characteristics. This can be particularly beneficial in stable environments where The parent’s traits are well-suited To survival.
Limitations & Challenges
While asexual reproduction has its advantages, it also comes with limitations & challenges. One significant drawback is The lack of genetic diversity among offspring. Without The shuffling of genes through sexual reproduction, offspring produced asexually may be more susceptible To environmental changes & disease.
Furthermore, asexual reproduction can limit The ability To adapt To changing conditions. Sexual reproduction allows for The creation of new gene combinations, increasing The potential for genetic variation & The acquisition of beneficial traits. In contrast, asexual reproduction only propagates existing genetic material without introducing new genetic possibilities.
Asexual Reproduction in The Natural World
Asexual reproduction can be observed in a wide range of animal species. Some notable examples include The bdelloid rotifers, microscopic organisms that have exclusively reproduced asexually for over 40 million years. These tiny creatures have adapted To their environment remarkably well & have successfully colonized various habitats.
In reptiles, several species can reproduce through parthenogenesis, such as some species of sharks, snakes, & lizards. Researchers have found that these reptiles can switch between sexual & asexual reproduction depending on environmental conditions, highlighting The flexibility & adaptability of asexual reproduction.
Exploring The Implications
The study of asexual reproduction in animals has significant implications for evolutionary biology & conservation efforts. By understanding The mechanisms & advantages of asexual reproduction, researchers can gain insights into The genetic & ecological factors that shape animal populations.
Understanding asexual reproduction also allows scientists To explore The potential for artificial forms of reproduction in endangered species. Techniques such as parthenogenesis induction offer The possibility of restoring populations without relying on a dwindling number of individuals.
In conclusion, asexual reproduction is a fascinating & diverse phenomenon observed in various animal species. It offers advantages such as rapid reproduction & The preservation of successful traits. However, it also poses challenges, particularly with regards To genetic diversity & adaptation. Exploring The world of asexual reproduction provides valuable insights into The intricate mechanisms of life & The remarkable diversity of The animal kingdom.
For more information on animal reproduction & development, you can visit this link.
Source: OpenStax Biology.
Key Features of Asexual Reproduction in Animals:
- Efficient & rapid reproduction process
- Preservation of successful traits
- Limited genetic diversity among offspring
- Possibility for artificial reproduction in conservation efforts
- Implications for evolutionary biology & population dynamics

What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is a process in which an organism produces offspring that are genetically identical To itself without The involvement of gametes or The fusion of genetic material from two different parents.
How do animals reproduce asexually?
Animals can reproduce asexually through various methods such as binary fission, budding, fragmentation, or parthenogenesis. These methods allow animals To produce offspring without The need for a mate.
What is binary fission?
Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction in which an organism divides into two separate individuals of roughly equal size. This is commonly observed in single-celled organisms like bacteria & protists.
What is budding?
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new individual grows out of a parent organism & eventually detaches To become an independent organism. This is commonly seen in certain invertebrates like hydras & yeast.
What is fragmentation?
Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction in which an organism breaks into several pieces, each of which can potentially grow into a new individual. This method is observed in certain worms, starfish, & plants.
What is parthenogenesis?
Parthenogenesis is a process of asexual reproduction in which an unfertilized egg develops into a new individual. This phenomenon is observed in some reptiles, insects, & fish species.
Why do animals reproduce asexually?
Animals reproduce asexually for various reasons, including The lack of available mates, The ability To colonize new habitats quickly, & The conservation of advantageous genetic traits. Asexual reproduction can be a more efficient method of reproduction in certain situations.
Are there any disadvantages To asexual reproduction?
While asexual reproduction can have advantages, there are also disadvantages. With a lack of genetic variation, offspring may be more susceptible To environmental changes & diseases. Additionally, asexual reproduction limits The potential for evolution & adaptation To new conditions.
Can animals that reproduce asexually also reproduce sexually?
Yes, many animals that reproduce asexually also have The ability To reproduce sexually. This flexibility allows them To employ different reproductive strategies depending on The circumstances, such as The availability of mates or The need for genetic diversity.
Are humans capable of asexual reproduction?
No, humans do not possess The ability for asexual reproduction. Reproduction in humans, as well as in most mammals, involves sexual reproduction, which requires The fusion of genetic material from two parents.
Exploring The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals
A Brief Overview
Asexual reproduction, also known as parthenogenesis, is a reproductive strategy used by certain animals To reproduce offspring without The need for fertilization. This intriguing phenomenon occurs in various species across The animal kingdom & presents a unique perspective on The diverse ways in which life can reproduce & perpetuate itself. Unlike sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction involves The production of offspring that are genetically identical or nearly identical To The parent. This article delves into The captivating world of asexual reproduction in animals, shedding light on its mechanisms, advantages, & examples in different species.
Mechanisms of Asexual Reproduction
There are several mechanisms through which asexual reproduction can occur in animals. One common method is through binary fission, where an organism physically splits into two separate entities, each capable of growing into a fully functional individual. This method is commonly observed in simple organisms such as bacteria & some species of single-celled organisms. Another form of asexual reproduction is budding, where a new offspring grows from a small projection or bud on The parent organism. This process is often seen in cnidarians like corals & jellyfish. Additionally, some animals can reproduce asexually through The production of specialized cells called gametes, which develop into new individuals without The need for fertilization.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction offers several advantages To animals that employ this method. Firstly, it allows for quick & efficient reproduction, as there is no need To search for mates or engage in complex courtship rituals. This is particularly advantageous in environments where suitable mates may be scarce or hard To find. Additionally, asexual reproduction ensures that beneficial traits & adaptations are directly passed on To offspring without The risk of dilution through genetic recombination. This can enhance The survival & success of a species, especially in stable & predictable environments. Furthermore, asexual reproduction can enable organisms To colonize new habitats rapidly & adapt To diverse ecological niches.
Examples of Asexual Reproduction in Animals
A variety of animals exhibit asexual reproduction, showcasing The remarkable adaptability & resilience of life. Invertebrates such as starfish & sea anemones are known To reproduce through processes like fragmentation, where a piece of an organism can regenerate into a complete individual. Some reptiles, such as certain species of lizards & snakes, can reproduce asexually through a process called parthenogenesis. In this process, unfertilized eggs develop into embryos & eventually hatch into offspring. Parthenogenesis has also been observed in certain fish species, including sharks & rays. Even some mammals, like certain species of sharks, have The capacity for asexual reproduction.
A Comparison of Sexual & Asexual Reproduction
| Aspect | Sexual Reproduction | Asexual Reproduction |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Diversity | High | Low |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Complexity | Higher | Lower |
| Adaptability | Greater | Varies |
| Survival | Depends on genetic diversity | Depends on stability of environment |
Exploring Parthenogenesis in Depth
Parthenogenesis, The ability of females To reproduce without fertilization, has captured The interest of scientists for many years. This process has been observed in various species, including insects, reptiles, & even birds. While it was long believed that mammalian parthenogenesis was impossible, recent studies have presented evidence To The contrary. The study of parthenogenesis in animals provides valuable insights into The genetic & physiological mechanisms underlying reproduction & development. Researchers continue To explore this fascinating phenomenon To deepen our understanding of The intricate world of reproduction.
A Glimpse into The Future
As our knowledge & understanding of asexual reproduction in animals continue To expand, we uncover a world of possibilities & implications. The study of asexual reproduction not only broadens our understanding of The natural world but also offers potential applications in fields such as agriculture & medicine. By deciphering The mechanisms & advantages of asexual reproduction, we may gain insights into developing more efficient breeding programs for agricultural species or even finding novel approaches To human reproductive technologies.
Conclusion
The exploration of The fascinating world of asexual reproduction in animals provides a captivating glimpse into The diverse & remarkable ways in which life perpetuates itself. From simple organisms To complex vertebrates, asexual reproduction offers unique advantages & challenges that have shaped The course of evolution. By understanding these processes, we gain a deeper appreciation for The intricacies of reproduction & The incredible adaptability of life on Earth.
Finally, in my own experience exploring The topic of asexual reproduction in animals, I was mesmerized by The multitude of strategies & adaptations that have evolved in different species. It is truly a testament To The ingenuity of nature & The endless possibilities for survival & reproduction in The animal kingdom.
Sources:
– Treehugger
– National Geographic
– Animal Tips
Conclusion
In conclusion, The world of asexual reproduction in animals is truly fascinating. We have explored various examples of animals that rely on this unconventional method To perpetuate their species. From budding To parthenogenesis, each process offers unique insights into The marvels of nature.
One of The most intriguing aspects of asexual reproduction is The ability of certain animals To produce offspring without The need for a mate. This can be advantageous in certain situations, such as The absence of suitable mates or The need for rapid population growth. The ability To reproduce without The energy-consuming process of finding a mate & engaging in sexual reproduction can provide a significant advantage for these animals.
Furthermore, asexual reproduction allows for genetic stability. Unlike sexual reproduction, which involves The recombination of genetic material, asexual reproduction produces offspring that are essentially clones of The parent. This can ensure The preservation of beneficial traits & adaptations within a population.
However, there are also limitations To asexual reproduction. The lack of genetic diversity can make a population more vulnerable To environmental changes & diseases. Without The variety provided by sexual reproduction, a species may struggle To adapt To new conditions, ultimately limiting its survival.
Despite these challenges, asexual reproduction has proven To be a successful reproductive strategy for numerous animal species. It highlights The adaptability & resilience of nature, showcasing The myriad ways in which organisms have evolved To ensure their survival.
Exploring The world of asexual reproduction in animals provides us with a deeper understanding of The incredible diversity & complexity of life on Earth. It allows us To marvel at The ingenuity of nature & appreciate The unique ways in which different species have evolved To overcome reproductive challenges.
In conclusion, asexual reproduction in animals is a captivating phenomenon that highlights The remarkable yet diverse strategies employed by nature To propagate life. By studying these intricate processes, we gain a newfound appreciation for The wonders of The animal kingdom & its fascinating reproductive strategies.