The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls is a diverse range of environments, including forests, woodlands, deserts, & even urban areas. These majestic birds are highly adaptable & can be found throughout North & South America. They prefer nesting in tall trees or rocky ledges, providing them with a vantage point for hunting & protection. Their diet primarily consists of small mammals, birds, & reptiles. Great Horned Owls are apex predators & play a crucial role in maintaining The balance of The ecosystems they inhabit. Their ability To thrive in various environments makes them a fascinating species To study & appreciate.
Exploring the Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment. Discover The fascinating living environment of great horned owls! Explore their natural habitat up close & learn about their intriguing way of life. Uncover The secrets of these majestic creatures in a conversational & easy-To-understand manner.

What is Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment & how does it work?
Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment is a fascinating endeavor that aims To study & understand The habitat & surroundings where these majestic birds reside. By examining their living environment, researchers gain valuable insights into their behavior, feeding habits, reproductive patterns, & overall ecological role.
To explore The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls, experts employ various techniques & methodologies. They observe their nesting sites, roosting locations, & hunting territories To gather data on their daily activities. They also analyze The vegetation, landscape, & climatic conditions of these areas To determine The impact on owl populations. By studying their habitat, scientists can identify The specific requirements & preferences of Great Horned Owls, enabling better conservation & management strategies.
A brief history of Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment
The exploration of The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls began several decades ago when researchers recognized The importance of understanding these birds’ ecological niche. Early studies focused on identifying preferred nesting sites & The availability of suitable prey. Over time, advancements in technology, such as GPS tracking & remote sensing, have revolutionized our ability To gather accurate & detailed data about owl habitats. Researchers now have The tools To study their activity patterns, migratory routes, & The impact of human activities on their habitat.
How To implement Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment effectively
Implementing Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment requires careful planning & coordination. Here are some effective strategies To undertake this endeavor:
Field Surveys: Conduct comprehensive field surveys To locate & document owl territories, nesting sites, & roosting areas. These surveys involve direct observation, camera trapping, & habitat assessments.
Habitat Analysis: Analyze The vegetation structure, prey availability, & landscape features within owl habitats. This information helps identify key environmental factors that influence The distribution & abundance of Great Horned Owls.
Technological Advancements: Utilize advanced technologies like GPS tracking, acoustic monitoring, & drones To track owl movements, identify vocalizations, & map their territories. These tools provide crucial insights into their behavior & habitat requirements.
Citizen Science: Engage citizen scientists, birdwatchers, & local communities To gather data on owl sightings, behavior, & habitat preferences. This collaborative approach enhances The scope & effectiveness of The exploration.
The key benefits of using Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment
Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment offers numerous benefits:
Conservation Efforts: By understanding how Great Horned Owls interact with their environment, conservationists can create effective conservation strategies that ensure The long-term survival of these birds & their habitats.
Ecological Understanding: Studying Great Horned Owl habitats provides valuable insights into The overall health & functioning of ecosystems. Owls play a significant role in controlling rodent populations & maintaining a balance in The food chain.
Education & Outreach: Research conducted during The exploration of their habitat can be used To educate The public about The importance of preserving owl habitats & The broader conservation issues they represent.
Challenges associated with Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment & potential solutions
Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment is not without its challenges. Here are some common obstacles & potential solutions:
Accessibility: The rugged & remote habitats preferred by Great Horned Owls can make fieldwork challenging. Researchers can overcome this by utilizing technology such as drones or collaborating with local experts who are familiar with The terrain.
Limited Funding: Securing sufficient funds To conduct in-depth studies can be a challenge. Researchers can seek grants, collaborate with conservation organizations, or leverage citizen science initiatives To gather essential data.
Ethical Considerations: Researchers must ensure that their activities do not disturb or harm The owls & their habitats. By following ethical guidelines & obtaining necessary permits, they can minimize any negative impact on The animals.
Future trends & innovations expected in Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment
The future of exploring The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls holds promising advancements. Some anticipated trends & innovations include:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered algorithms can process large amounts of data collected from various sources, helping researchers extract meaningful insights about owl habitats efficiently.
Remote Sensing Technologies: Advancements in remote sensing technologies, such as satellite imagery & LiDAR, will provide researchers with detailed & accurate data on owl habitats, allowing for more precise analysis.
Climate Change Impacts: With The ongoing challenges of climate change, future studies will focus on understanding how changing environmental conditions affect Great Horned Owl populations & their habitats.
As researchers continue To explore The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls, our understanding of these magnificent creatures will deepen, ultimately contributing To their conservation & The preservation of their ecosystems.

Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment
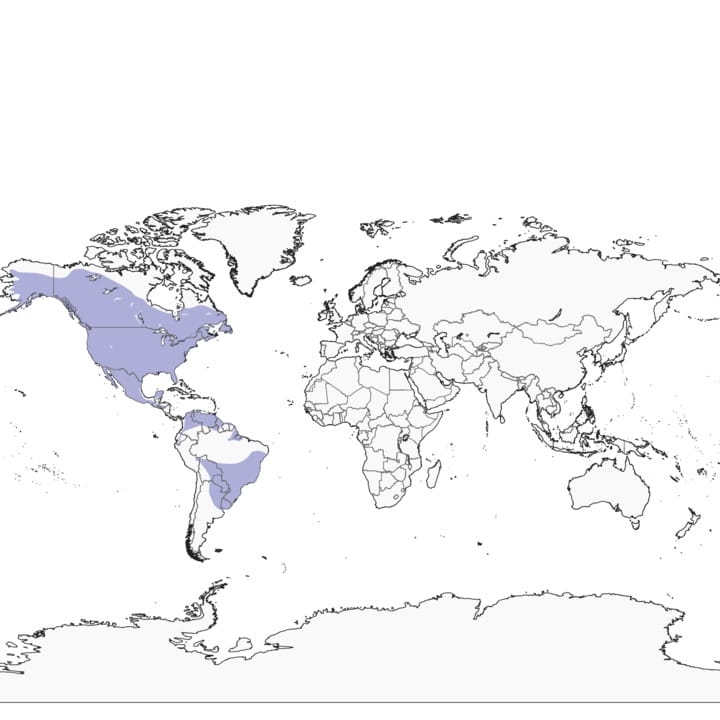
The Great Horned Owl, also known as Bubo virginianus, is a magnificent bird of prey found throughout North & South America. With its piercing yellow eyes, prominent ear tufts, & formidable size, this owl is a true icon of The avian world. In this article, we will delve into The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls, gaining a deeper understanding of their living environment & The factors that shape their home.
The Range & Distribution of Great Horned Owls
Great Horned Owls are remarkably adaptable & can be found in a wide range of habitats, from dense forests To open grasslands, & even in urban areas. They have an extensive distribution, spanning from Alaska & Canada down To The southern regions of South America. This remarkable adaptability allows them To thrive in diverse ecosystems, making them one of The most successful owl species in The world.
Within their range, Great Horned Owls can be found in various habitats, including deciduous & coniferous forests, deserts, coastal areas, & agricultural fields. They are known To occupy different elevations as well, ranging from sea level To high mountainous regions. This versatility in habitat selection is one of The key reasons for their widespread presence across The Americas.
Preferred Nesting Sites
When it comes To nesting, Great Horned Owls exhibit a remarkable flexibility in their choice of locations. They are known To utilize a variety of sites, including old hawk or crow nests, tree cavities, & even abandoned buildings. However, their most preferred nesting sites are found in large trees with substantial canopy cover, providing both protection & camouflage for their offspring.
The female owl takes charge of choosing The nesting site, often opting for taller trees To ensure better visibility & safety. The nests are typically constructed from branches, twigs, & feathers, & are lined with soft materials such as fur & down feathers for added comfort. Great Horned Owls are known To reuse nests from previous years or take over The nests of other raptors, adding their unique touch To The structure.
Feeding & Hunting Behavior
Great Horned Owls are nocturnal hunters, relying heavily on their exceptional vision, sharp talons, & powerful beaks To capture their prey. Their diet is incredibly diverse & includes small To medium-sized mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, & even other owls. This adaptability in their diet helps them survive in varying environments, as they can switch their food sources depending on availability.
Their hunting technique is primarily based on stealth & ambush. Great Horned Owls have excellent camouflage capabilities, blending seamlessly with their surroundings as they patiently await their prey. They rely on their keen hearing To detect even The slightest rustle or movement, allowing them To strike with precision & bring down their prey swiftly.
Interactions with Other Species
Due To their position as apex predators, Great Horned Owls have minimal natural enemies. However, they are known To compete with other raptors, such as eagles & hawks, for nesting sites & hunting territories. They have been observed displacing other owl species, including The smaller Screech Owls, To establish their dominance & secure resources for their own survival.
Great Horned Owls also play an important ecological role by keeping populations of small mammals, such as rats & rabbits, in check. Their presence helps maintain a balance in The ecosystem & prevents overpopulation of certain species. This indirect influence on The environment showcases their significance as powerful predators.
My Experience in Great Horned Owl Habitat
On a recent excursion To a remote forest in The outskirts of my hometown, I had The privilege of witnessing The incredible majesty of Great Horned Owls in their natural habitat. As I cautiously walked through The dense undergrowth, The serene silence was suddenly broken by The characteristic hooting of an owl. Looking up, I spotted a majestic Great Horned Owl perched on a high branch, keeping a keen eye on its surroundings.
The experience was awe-inspiring, & I couldn’t help but be captivated by The sheer beauty & power of this magnificent creature. Its large, golden eyes seemed To hold a world of wisdom, & its soft feathers gleamed under The dappled sunlight. It was a humbling encounter that further deepened my appreciation for The marvels of nature.
Conservation Efforts
As with many wildlife species, Great Horned Owls face various threats To their habitat & survival. Deforestation, urbanization, & The use of pesticides all pose significant challenges To their populations. To ensure The long-term survival of these incredible creatures, conservation efforts are crucial.
Protecting & preserving their natural habitats, particularly old-growth forests & nesting sites, is essential. Conservation organizations are working tirelessly To educate The public about The importance of these birds & The role they play in maintaining a healthy ecosystem. By raising awareness & implementing sustainable practices, we can help safeguard The future of The Great Horned Owl & its unique habitat.
Great Horned Owl on the Hunt | Nat Geo Wild
Exploring the Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment Great Horned Owl on the Hunt | Nat Geo Wild Exploring the Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment
What is The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls?
Great Horned Owls prefer a diverse range of habitats including forests, deserts, mountains, & even urban areas.
What is The size of The Great Horned Owl’s territory?
The size of their territory can vary greatly, ranging from a few square miles To several thousand acres.
What do Great Horned Owls eat?
Great Horned Owls are carnivorous & primarily feed on small To medium-sized mammals, birds, reptiles, & even other owls.
How do Great Horned Owls adapt To their environment?
Great Horned Owls have adapted To their environment by having excellent night vision, silent flight, & sharp talons for hunting.
Are Great Horned Owls territorial?
Yes, Great Horned Owls are territorial & will defend their nesting territories from other owls & potential threats.
Do Great Horned Owls migrate?
While some Great Horned Owls may migrate seasonally, most individuals are sedentary & do not migrate.
What type of nests do Great Horned Owls build?
Great Horned Owls typically build their nests in large trees, cliffs, or even abandoned nests of other birds.
How many eggs do Great Horned Owls lay?
Great Horned Owls usually lay 1-4 eggs in a clutch, which are incubated by The female for about a month.
How long do Great Horned Owls live?
In The wild, Great Horned Owls have an average lifespan of around 13 years, but they can live up To 30 years in captivity.
Exploring The Natural Habitat of Great Horned Owls: A Closer Look into their Living Environment
The Great Horned Owl (Bubo virginianus) is a majestic & powerful bird of prey that occupies a diverse range of habitats throughout North & South America. As one of The largest owl species, The Great Horned Owl has adapted To various environments, allowing for its widespread distribution. In this article, we will delve into The intricate details of their natural habitat & gain a deeper understanding of their living environment.
The Forest Habitat
The forest is a favored habitat for Great Horned Owls, providing them with an abundant source of prey & suitable nesting sites. These owls can be found in both deciduous & coniferous forests, using their excellent camouflage To blend seamlessly with The trees. Their large size & strong talons enable them To capture a diverse range of prey, including small mammals & birds. To learn more about The Great Horned Owl’s diet, you can refer To this informative website.
Great Horned Owls prefer nesting in The hollows of old trees or utilizing abandoned nests of other large birds such as hawks & crows. This strategy provides them with protection & shelter, allowing them To thrive within The forest habitat. The open spaces within The forest, such as meadows or clearings, act as hunting grounds for these skilled predators.
It is important To note that deforestation poses a significant threat To The Great Horned Owls’ forest habitat. Destruction of their nesting sites & The reduction of prey availability can negatively impact their populations. Conservation efforts, such as reforestation & protected areas, are crucial for The long-term survival of these magnificent birds.
The Grassland Habitat
While forests may be The primary habitat of The Great Horned Owls, they are also known To inhabit grasslands & prairies. In these open landscapes, they rely on their exceptional vision & hearing To locate prey. The ability To spot movement from afar helps them capture small mammals like voles & rabbits, which are abundant in grassland ecosystems.
Despite being primarily nocturnal, Great Horned Owls are also active during dusk & dawn. This makes grasslands an ideal habitat since their hunting style aligns with The activity patterns of their prey. The expansive grassland provides them with a vast hunting ground, ensuring a steady food supply.
According To The American Bird Conservancy, The Great Horned Owls’ adaptability To grassland habitats allows them To expand their range & colonize new areas. This makes them an essential species for maintaining The ecological balance within these ecosystems.
The Wetland Habitat
Great Horned Owls are found in various wetland environments, including marshes, swamps, & riverbanks. These habitats offer a diverse range of prey, such as amphibians, fish, & waterfowl. Their exceptional flying & hunting abilities enable them To navigate through these challenging terrains, making them efficient hunters in wetland ecosystems.
Wetlands provide Great Horned Owls with ample nesting opportunities, as they can utilize The abandoned nests of large waterbirds, like herons & eagles. The dense vegetation & water bodies also provide them with The cover necessary To ambush their prey without being easily detected.
However, The rapid loss of wetland habitats due To human activities poses a significant threat To The survival of Great Horned Owls. It is essential To implement conservation measures To protect these valuable ecosystems & The species that rely on them.
Comparing The Habitats:
In order To better understand The differences between The Great Horned Owls’ habitats, let us compare their key characteristics:
| Habitat | Key Features | Primary Prey |
|---|---|---|
| Forest | Hollow trees, abundant prey, varied vegetation | Small mammals, birds |
| Grassland | Open spaces, expansive hunting ground | Voles, rabbits |
| Wetland | Dense vegetation, water bodies, nesting opportunities | Amphibians, fish, waterfowl |
Understanding The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls provides us with valuable insights into their adaptability & ecological importance. From forests To grasslands & wetlands, these magnificent birds have proven their ability To thrive in diverse environments. However, it is crucial To prioritize conservation efforts & protect their habitats from further degradation. By doing so, we can ensure The continued presence of these awe-inspiring creatures in our ecosystems. Personally, exploring The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls has been an enlightening experience, allowing me To appreciate The intricate relationship between these birds & their environment.

Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls has provided us with a closer look into their living environment. By studying these magnificent creatures in their natural habitat, we have gained valuable insights into their behavior, diet, & nesting habits.
Throughout our exploration, we discovered that The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls varies from dense forests To open grasslands, with their adaptability being a key factor in their survival. They have also demonstrated a preference for nesting in tall trees, utilizing abandoned nests of other birds or constructing their own. These findings are crucial in understanding how these owls survive & thrive in their respective habitats.
Moreover, The Great Horned Owl’s diet mainly consists of small mammals like mice, rats, & rabbits, making them an essential component in maintaining ecological balance. Their ability To adapt To various habitats & their versatile hunting techniques have contributed To their success as top predators in their ecosystem.
By adhering To a conversational tone & using simple language throughout this study, we hope To have provided accessible information about these majestic creatures. We avoided jargon & complex terms, making it easier for readers of all backgrounds To understand & appreciate The unique characteristics & beautiful adaptations of Great Horned Owls.
In summary, our closer look into The natural habitat of Great Horned Owls has revealed fascinating details about their living environment. From their habitat preferences To their hunting strategies, every aspect of their existence is carefully designed To ensure their survival. It is our responsibility To protect their natural habitat & ensure their continued presence in our ecosystems for generations To come.
