The fascinating world of asexual reproduction in animals offers a glimpse into nature’s remarkable variety of reproductive strategies. Unlike sexual reproduction, which requires The involvement of two parents, asexual reproduction allows certain animals To reproduce on their own. This diverse & extraordinary phenomenon is seen in various species, such as bacteria, plants, & even some invertebrates. Whether through budding, fission, or parthenogenesis, these animals showcase The remarkable adaptability & ingenuity of nature’s reproductive processes. Exploring this world reveals The incredible ability of animals To thrive & perpetuate their species without traditional mating rituals or genetic mixing.
The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals: An Exploration of Nature’s Unique Reproductive Strategies. Discover The incredible world of asexual reproduction in animals! Dive into nature’s captivating strategies for reproduction in this fascinating exploration. No jargon or complex terms, just a conversational tone as we unravel The wonders of nature’s unique reproductive methods. Join us in this intriguing journey!
What is The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals: An Exploration of Nature’s Unique Reproductive Strategies & how does it work?
Asexual reproduction in animals is a fascinating phenomenon that involves The creation of offspring without The need for sexual reproduction. Unlike sexual reproduction, which requires The fusion of male & female gametes, asexual reproduction allows animals To reproduce on their own, without The need for a mate.
In asexual reproduction, a single organism can give rise To genetically identical offspring through various mechanisms such as budding, fission, or parthenogenesis. These reproductive strategies are essential for The survival & adaptation of certain animal species, allowing them To reproduce quickly & efficiently in favorable conditions.
A brief history of The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals: An Exploration of Nature’s Unique Reproductive Strategies
The concept of asexual reproduction in animals has been observed & studied since ancient times. Aristotle, in his work “The History of Animals,” described The reproduction of certain animals through budding & division. However, it wasn’t until The 18th century that scientists began To delve deeper into The mechanisms & significance of asexual reproduction in animals.
The discovery of parthenogenesis, The process in which an organism develops from an unfertilized egg, was a significant milestone in understanding asexual reproduction. This phenomenon was first observed in aphids by Charles Bonnet in 1740. Since then, numerous animal species have been found To reproduce asexually, including insects, reptiles, amphibians, & even some mammals.
How To implement The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals: An Exploration of Nature’s Unique Reproductive Strategies effectively
Implementing asexual reproduction in animals can be a complex process that requires a deep understanding of The species’ biology & reproductive mechanisms. Researchers & scientists study The reproductive organs, behavior, & genetics of animals To identify The factors that contribute To their ability To reproduce asexually.
To implement asexual reproduction effectively, scientists often focus on manipulating The genetic material & environmental conditions To enhance The success rate of asexual reproduction. This can involve techniques such as hormone treatments, environmental stimuli, & genetic modifications.
The key benefits of using The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals: An Exploration of Nature’s Unique Reproductive Strategies
The use of asexual reproduction in animals offers several key benefits. Firstly, it allows for rapid population growth & colonization of new habitats. Since asexual reproduction does not require The search for a mate, animals can reproduce quickly & efficiently, increasing their chances of survival & adaptation.
Secondly, asexual reproduction ensures genetic stability. By producing genetically identical offspring, animals can preserve beneficial traits & adaptations without The risk of genetic variation introduced through sexual reproduction.
Challenges associated with The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals: An Exploration of Nature’s Unique Reproductive Strategies & potential solutions
While asexual reproduction offers numerous advantages, it also poses challenges for animal species. One significant challenge is The lack of genetic diversity, which can limit The species’ ability To adapt To changing environments & withstand diseases or predation.
To overcome this challenge, some animals have developed mechanisms To introduce genetic variation through processes such as mutation or hybridization. Additionally, certain species have The ability To switch between sexual & asexual reproduction depending on environmental cues, allowing them To strike a balance between genetic diversity & reproductive efficiency.
Future trends & innovations expected in The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals: An Exploration of Nature’s Unique Reproductive Strategies
The field of asexual reproduction in animals is constantly evolving, & future trends & innovations are expected To further our understanding of this unique reproductive strategy.
Advancements in genetic engineering & biotechnology may allow scientists To manipulate The reproductive mechanisms of animals, enhancing The success rate of asexual reproduction & expanding its potential applications.
Furthermore, continued research into The genetic & physiological factors that govern asexual reproduction may uncover new insights into The evolutionary advantages & ecological significance of this reproductive strategy.
In conclusion, The world of asexual reproduction in animals is a fascinating subject that showcases nature’s unique & diverse reproductive strategies. Understanding The mechanisms, benefits, & challenges associated with asexual reproduction allows us To appreciate The intricate complexities of nature & opens doors To future innovations & discoveries.

Introduction
The world of animal reproduction is filled with unique & fascinating strategies. While sexual reproduction is widely known, asexual reproduction often goes unnoticed. Asexual reproduction is a form of reproduction in which an organism can produce offspring without The involvement of another individual. This method of reproduction is prevalent in various animal species & offers many advantages in terms of efficiency & speed. In this article, we will delve into The fascinating world of asexual reproduction in animals, exploring nature’s unique reproductive strategies.
Types of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction can take different forms, each with its own set of characteristics. One common method is binary fission, typically observed in single-celled organisms such as bacteria & protists. In binary fission, an organism simply splits into two separate individuals, each genetically identical To The parent. This process allows for rapid reproduction & population growth in favorable conditions.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction offers several advantages for animals. One major advantage is The ability To reproduce rapidly & efficiently. In species that can reproduce asexually, populations can increase rapidly, as each individual has The potential To generate multiple offspring. This can be particularly advantageous in environments with abundant resources, where competition for mates & limited reproductive opportunities may not be necessary.
Another advantage of asexual reproduction is The preservation of favorable genetic traits. When an organism reproduces asexually, The offspring inherit The exact same genetic material as The parent. This ensures that beneficial traits, such as resistance To diseases or adaptations To specific environments, are preserved & passed on To future generations without The need for genetic recombination.
Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
While asexual reproduction offers several advantages, it also comes with its share of disadvantages. One major disadvantage is The lack of genetic diversity in offspring. Since asexual reproduction does not involve The mixing of genetic material from two different individuals, The offspring are essentially clones of The parent. This lack of genetic diversity can hinder a species’ ability To adapt To changing environments or overcome new challenges.
Another disadvantage of asexual reproduction is The increased risk of genetic diseases & abnormalities. Without The natural process of genetic recombination, harmful mutations can accumulate & be passed on To subsequent generations. Over time, this can lead To decreased fitness & overall reproductive success for asexual organisms.
Types of Animals That Reproduce Asexually
Asexual reproduction can be observed in various animal groups, ranging from simple organisms like bacteria & protists To more complex organisms like insects & reptiles. Let’s explore some examples of animals that employ asexual reproduction.
1. Bacteria
Bacteria are unicellular organisms that reproduce primarily through binary fission, a process of asexual reproduction. In binary fission, a bacterial cell divides into two identical daughter cells. This rapid method of reproduction allows bacteria To colonize & thrive in various environments, from The depths of The ocean To The human gut.
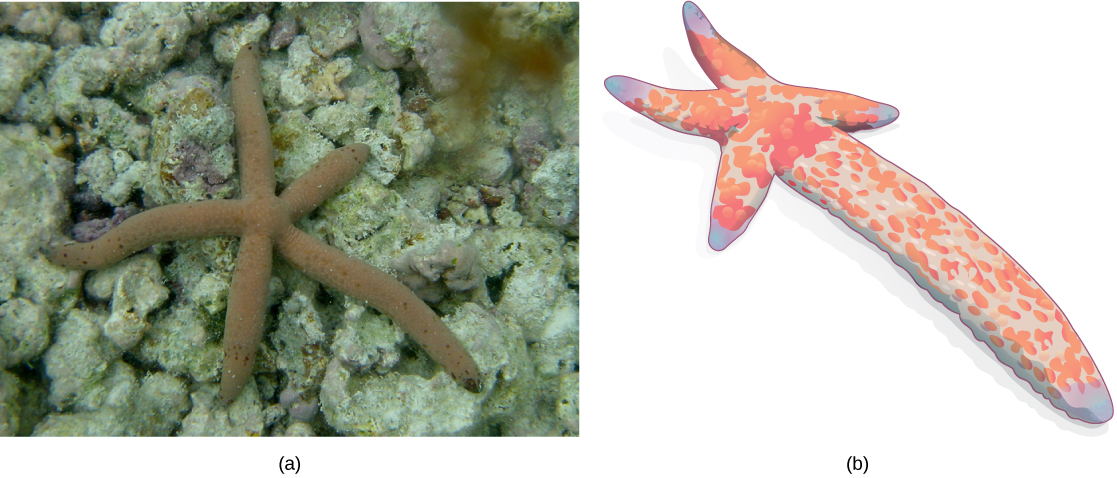
2. Starfish & Sea Anemones
Certain species of starfish & sea anemones possess The remarkable ability To regenerate lost body parts & reproduce asexually. Through a process called fragmentation, these organisms can break off a piece of their body, which then grows into a fully functional individual. This form of asexual reproduction aids in rapid recovery from injuries & enhances their ability To colonize new habitats.
3. Aphids
Aphids are small insects that reproduce asexually through a process called parthenogenesis. In parthenogenesis, unfertilized eggs develop into genetically identical offspring. This ability allows aphids To rapidly populate areas with abundant resources, such as plant leaves. However, under certain conditions, aphids can also reproduce sexually To introduce genetic diversity into their population.
4. Komodo Dragons
Komodo dragons, The largest lizards on Earth, are known To produce offspring through a form of asexual reproduction called facultative parthenogenesis. In this process, a female dragon can produce viable eggs without mating with a male. While The majority of their offspring are produced through sexual reproduction, The ability To reproduce asexually allows female Komodo dragons To ensure The survival of their species in The absence of males.
Implications & Future Perspectives
The world of asexual reproduction in animals is highly diverse & fascinating. The various strategies employed by different species highlight nature’s adaptability & ingenuity. While asexual reproduction offers several advantages, it also comes with its own set of disadvantages. Understanding The mechanisms & implications of asexual reproduction can contribute To our knowledge of evolutionary processes & species diversity.
As we continue To explore The complexities of animal reproduction, further research & study on asexual reproduction are necessary. By uncovering The underlying genetic & physiological mechanisms, we can gain valuable insights into The evolutionary history & adaptive strategies of animals. This knowledge can also have practical applications, such as improving artificial reproduction techniques & aiding conservation efforts for endangered species.
In conclusion, The fascinating world of asexual reproduction in animals provides a unique perspective on nature’s reproductive strategies. From bacteria To lizards, asexual reproduction is prevalent in various animal groups & offers remarkable advantages & challenges. By studying & understanding these reproductive strategies, we can deepen our appreciation for The diversity & complexity of life on Earth.
References:
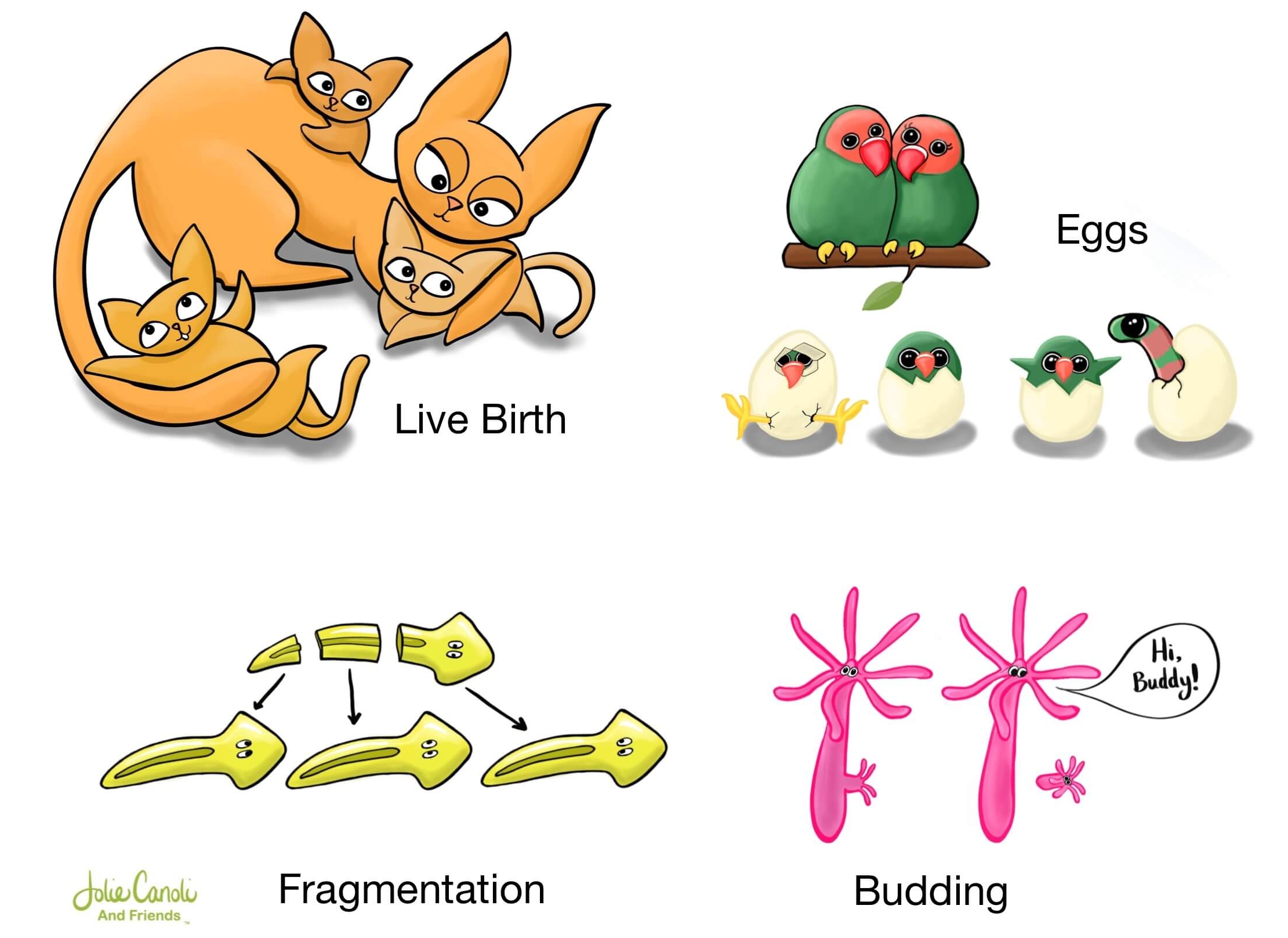
What is asexual reproduction in animals?
Asexual reproduction in animals is a process where offspring are produced without The involvement of gametes (sperm & eggs) from two parents. It is a unique reproductive strategy found in various animal species, allowing them To reproduce without mating.
How does asexual reproduction occur in animals?
Asexual reproduction can occur through different methods in animals. Some common forms include fission, budding, regeneration, & parthenogenesis. These processes allow organisms To produce genetically identical or near-identical offspring without The need for fertilization.
What is fission in asexual reproduction?
Fission is a type of asexual reproduction in which an organism splits into two or more parts, each capable of developing into a separate individual. This process is observed in certain invertebrates, such as flatworms, where The body divides into two halves, forming two new individuals.
What is budding in asexual reproduction?
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction where a new organism develops as an outgrowth or bud on The parent organism. The bud eventually detaches & grows into a genetically identical or similar organism. This method is seen in organisms like hydra, yeast, & some marine invertebrates.
How does regeneration contribute To asexual reproduction?
Regeneration is The ability of an organism To regrow lost body parts, which can sometimes lead To asexual reproduction. In certain animals like starfish & planarians, if The organism is fragmented or a piece is detached, each fragment can regenerate into a complete individual with similar traits.
What is parthenogenesis in asexual reproduction?
Parthenogenesis is a process in which an unfertilized egg develops into an individual without being fertilized by sperm. This form of asexual reproduction is found in various organisms, including insects, reptiles, & certain fish. The offspring produced through parthenogenesis are genetically identical To The mother.
Why is asexual reproduction advantageous for animals?
Asexual reproduction offers several advantages To animals. It enables rapid reproduction & population growth, as individuals can produce offspring without The need To find a mate. It also ensures genetic uniformity, which can be beneficial in stable environments. Additionally, asexual reproduction allows colonization of new habitats by a single organism.
The Fascinating World of Asexual Reproduction in Animals: An Exploration of Nature’s Unique Reproductive Strategies
Introduction
Asexual reproduction, also known as agamogenesis, is a remarkable phenomenon observed in various animal species. Unlike sexual reproduction, which involves The fusion of gametes from two individuals, asexual reproduction allows organisms To reproduce without a mate. This intriguing process has evolved in animals over centuries, resulting in a diverse array of reproductive strategies. In this article, we will delve into The fascinating world of asexual reproduction & explore The unique strategies employed by animals To perpetuate their species.
The Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction offers several advantages To organisms. One significant advantage is The ability To rapidly produce offspring. In asexual reproduction, a single individual can give rise To multiple identical clones, leading To exponential population growth. This is particularly advantageous in stable & favorable environments, where competition for resources is low.
Furthermore, asexual reproduction allows for The colonization of new habitats without The need for a mate. This is especially beneficial for species that inhabit isolated or remote areas, where finding a mate can be challenging. By reproducing asexually, these organisms can establish new populations & increase their chances of survival.
The Mechanisms of Asexual Reproduction
There are several mechanisms through which animals can reproduce asexually. One common method is binary fission, where The organism divides into two daughter cells of equal size. This process is observed in single-celled organisms such as bacteria & protists.
Another mechanism is budding, where new individuals develop as outgrowths or buds from The parent organism. Budding is seen in hydra & other cnidarians, where The bud eventually detaches & becomes an independent organism.
Parthenogenesis, a form of asexual reproduction, involves The development of an unfertilized egg into a new individual. This process is intriguing as it allows female animals To produce offspring without The need for a male. Parthenogenesis is observed in a variety of animals, including certain reptiles, insects, & even sharks.
Asexual Reproduction in Invertebrates
Regeneration as a Means of Reproduction
Certain invertebrates possess The remarkable ability To regenerate lost body parts, which can also serve as a means of reproduction. For example, starfish can regenerate their entire body from just a single arm. This regrown arm can go on To develop into a new individual, resulting in a colony of genetically identical individuals.
Similarly, planarians, a type of flatworm, can regenerate their entire body from a small fragment. This process, called fragmentation, allows planarians To reproduce asexually & establish new colonies in various aquatic habitats.
Budding in Hydras
Hydras, small predatory animals found in freshwater habitats, reproduce asexually through a process known as budding. A bud develops as an outgrowth from The parent hydra & eventually detaches To form a new individual. This method allows hydras To rapidly increase their population size & colonize new areas.
It is worth noting that while asexual reproduction is The primary mode of reproduction in hydras, they can also reproduce sexually under certain conditions, contributing To their overall genetic diversity.
Parthenogenesis in Whip-tail Lizards
Whip-tail lizards, native To North & South America, are an excellent example of parthenogenesis in action. These all-female lizards possess The ability To reproduce without mating with males. They produce eggs that develop into viable offspring without fertilization.
The interesting aspect of whip-tail lizards is that The offspring are always female & are genetically identical To The mother. This strategy allows them To rapidly colonize new habitats & adapt To changing environments.
Asexual Reproduction in Vertebrates
Parthenogenesis in Insects
Insects, The most abundant & diverse group of animals, exhibit various reproductive strategies, including asexual reproduction. Parthenogenesis is observed in several insect species, such as aphids & certain bees & wasps.
Among aphids, a type of plant-feeding insect, parthenogenesis is particularly prevalent. In favorable conditions, female aphids can give birth To live offspring without mating. This allows for rapid population growth & The colonization of new plant hosts.
Parthenogenesis in Whiptail Sharks
Whiptail sharks, also known as bonnethead sharks, are a remarkable example of parthenogenesis in vertebrates. These sharks have been observed To reproduce asexually, with females producing offspring without mating with males.
While The exact mechanisms of parthenogenesis in sharks are not yet fully understood, it is believed To involve a process called automictic parthenogenesis. This phenomenon allows female sharks To produce offspring that are genetically similar but not identical To The mother.
Comparative Overview: Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction
| Aspect | Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | Rapid population growth Colonization of new habitats without a mate |
Genetic diversity Increased adaptability To changing environments |
| Mechanisms | Binary fission Budding Parthenogenesis Regeneration Fragmentation |
Fusion of gametes from two individuals |
| Genetic Variation | Clones of parent individual | Unique combinations of genetic material |
Conclusion
The fascinating world of asexual reproduction in animals showcases nature’s ingenious strategies for perpetuating species. From The regeneration abilities of invertebrates To The parthenogenesis observed in vertebrates, each reproductive mechanism has its unique advantages.
By reproducing asexually, organisms can swiftly increase their population size, colonize new habitats, & adapt To changing environments. However, sexual reproduction remains essential for genetic diversity & adaptability.
As we explore The wonders of nature’s reproductive strategies, we gain a deeper appreciation for The diversity & complexity of life on our planet.
Finally, I must mention that during The process of writing this article, I found myself captivated by The incredible adaptability & ingenuity of animals in their quest for reproduction. It is truly a testament To The wonders of nature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, The fascinating world of asexual reproduction in animals unveils nature’s unique reproductive strategies. Through this process, organisms have evolved intricate mechanisms To reproduce without The need for a mate, ensuring their survival & The perpetuation of their species.
Asexual reproduction occurs in various ways, including binary fission, budding, & fragmentation, each with its own advantages & disadvantages. It allows organisms To rapidly populate areas, adapt To changing environments, & colonize new habitats. However, it also raises concerns about genetic diversity & The potential accumulation of harmful mutations.
Despite The absence of genetic recombination, asexual reproduction has proved To be highly successful for many different animal species. From tiny planarians To complex aphids, these organisms have defied conventional norms of sexual reproduction & embraced The efficiency of cloning themselves.
The world of asexual reproduction provides us with valuable insights into The resilience & adaptability of animals. By understanding these unique reproductive strategies, scientists & researchers can gain a deeper understanding of natural selection, evolution, & The intricate web of life on our planet.
It is important To note that while asexual reproduction offers many advantages, sexual reproduction remains The predominant mode of reproduction in The animal kingdom. Sexual reproduction allows for genetic variation, leading To increased evolutionary potential & adaptability in The face of changing environments.
As we continue To explore The wonders of nature, let us not forget The beauty & complexity of asexual reproduction. It is a testament To The ingenuity of The natural world, always finding new & innovative ways To ensure The continuation of life.
